Retinal Laser Therapy
What Conditions Benefit from Retinal Laser Therapy?
Several conditions of the retina may require retinal laser to stop the progression of disease or minimize vision loss. Retina laser therapy is a versatile treatment option and one of the most common and widely used methods to treat many eye conditions. These conditions include:
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR):
Affecting individuals who have Type I or Type II diabetes, proliferative diabetic retinopathy is an advanced stage of diabetic retinopathy. Prolonged high levels of blood sugar or the duration of diabetes can lead to abnormal growth of blood vessels. These abnormal vessels, if left untreated, can lead to permanent vision loss by causing bleeding in the eye, retinal detachment, or severe glaucoma. The type of retinal laser therapy that is applied to PDR patients is known as panretinal photocoagulation (PRP). This extensive laser treatment is applied to the peripheral retina typically 360 degrees. This form of retinal laser can help suppress the harmful blood vessels in the retina and prevent them from growing again. PRP aids in reducing the long-term risk of vision loss from the growth of abnormal blood vessels.
Diabetic Macular Edema (DME):
The most common cause of vision loss in diabetics is diabetic macular edema. In this condition, blood vessels in the center of the retina are damaged by high blood sugar and blood pressure. The vessels begin to leak fluid into the retina, causing swelling in the macula. While this condition is most commonly treated with eye injections, some forms of DME respond well to focal laser, which is a small number of targeted laser spots that can shut down leaky vessels and reduce the accumulation of fluid in the retina.
Retinal Tear:
A retina tear is a serious condition that should be treated sooner rather than later. A retinal tear is a hole or rip in the retina, similar to a tear in a cloth. If left untreated it can lead to a retinal detachment – a condition in which the retina lifts away from the back of the eye. As we age, the vitreous gel in our eyes shrinks and pulls away from the back of the eye. During this normal aging process, the vitreous may pull on the retina causing a tear. If this occurs, you may experience a sudden onset of flashes or floaters. Once your ophthalmologist has completed a full dilated exam and identified a retinal tear, they may opt to apply retinal laser to the torn area. Retinal laser is used to seal the retina by creating a barrier around the tear that prevents fluid from entering the sub-retinal space through the tear.
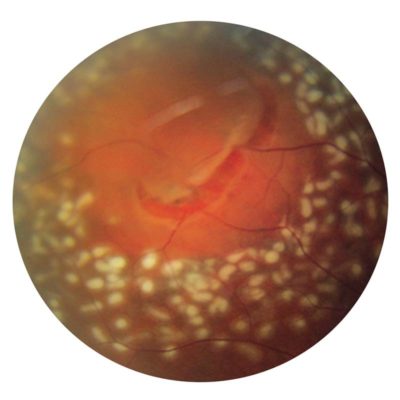
Retinal Vein Occlusions:
When a blood clot forms in a retinal vein, it prevents blood from flowing from the retina back to the heart. This is known as a retinal vein occlusion, sometimes referred to as a stroke in the eye.
The retinal nerve cells need a constant flow of blood to deliver the proper oxygen and nutrients. When this flow is disrupted, damage occurs, causing fluid leakage in the retina or hemorrhages (bleeding). Additionally, abnormal blood vessels may begin to grow causing retinal swelling (edema).
Without the proper treatment, a retinal vein occlusion can lead to irreversible loss of vision.
In some situations, your retinal specialist may recommend that you undergo retinal laser therapy. The laser can be applied to the central retinal to reduce the swelling of the retina. If there is a growth of new blood vessels, panretinal photocoagulation can be applied 360 degrees to suppress abnormal growth of new blood vessels in the retina.
What are the risks of Retinal Laser?
Retinal laser is a minimally invasive procedure that can prevent specific retinal diseases from progressing and causing more harm. However, as with any procedure, it is important to understand and accept the risks that may come with it. In the case of retinal laser, the procedure is relatively safe with minimal risk of complications. Complications that may arise during this procedure include:
- Temporary pain or ache of the eye during or after treatment
- Bleeding in the eye
- Decreased peripheral or night vision
- Retinal scarring
- Reduction in contrast sensitivity
- Need for retreatment
How Is Retinal Laser Therapy Performed?
Most conditions that can be treated by a retinal laser are diagnosed by undergoing a dilated eye exam. Your retinal specialist will conduct a full exam of the eye to see if retinal laser is the appropriate treatment option for your condition. In addition to a dilated eye exam, your ophthalmologist may elect to take photographs or other imaging tests such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) to monitor the progression of your condition. Once it’s been determined that a retinal laser is necessary to manage your eye, it is important to understand what to expect before, during, and after treatment.
Before:
Your retinal specialist will extensively discuss your current condition and why you may benefit from retinal laser. The risks, benefits, and alternatives will be discussed with you. Once you have an understanding, your retina specialist will ensure your eye is fully dilated to allow the best view of the retina. You can expect your pupil to remain dilated for a few hours following the procedure.
During:
Retinal laser is an in-office procedure that typically takes place the same day your diagnosis is given. Topical anesthetic drops will be given to reduce any discomfort felt at the time of the procedure. You will then lean back in the exam chair or be placed into a slit lamp. Your retina specialist will then use a special lens to direct the laser to the specific treatment area. You will then see a green laser beam and hear a series of beeps as the retina is being treated. Laser patients report sensitivity to brightness and intermittent pain from the laser shots. The entire treatment can last up to 15 minutes depending on the amount of laser needed.

After:
It’s important to follow any instructions given to you after having received retinal laser therapy. Common things to expect after undergoing retinal laser include:
- Sensitivity to light after due to dilation – wearing sunglasses while outside may allow these symptoms to subside.
- Soreness to the eye – Taking over-the-counter medicine will relieve any soreness felt after the laser.
- Blurred vision after laser
It’s important to notify your retinal specialist if you are experiencing any worsening vision, pain, redness, or swelling after retinal laser therapy.
Contact Us!
Dr. Anita Shane, founder and director of Venice Retina in Venice Florida, has years of training in diagnosing and treating retinal conditions that benefit from retinal lasers. She will walk you through the appropriate treatment that will provide you with the best visual outcome. If you have a retinal condition that would benefit from retinal laser therapy contact us today!
