Pneumatic Retinopexy
Procedures and Treatments for Eye Conditions in Venice, FL
Located in the back of the eye is the retina. This layer of the eyeball contains light sensitive cells that trigger impulses to the brain to produce the visual image you see. If the retina pulls away from its supporting tissue, a detachment occurs. When a retinal detachment occurs, the retina no longer functions properly. A retinal detachment is an eye emergency and needs to be treated immediately. Without immediate care, permanent vision loss is possible. One method of treating a retinal detachment is through an in-office procedure known as a pneumatic retinopexy.
What Is a Pneumatic Retinopexy?

A pneumatic retinopexy is an in-office procedure that is used to repair a retinal detachment and restore vision. During this procedure, your ophthalmologist will numb the eye to reduce any discomfort. A gas bubble is then injected into the vitreous cavity of the eye. You will then be positioned to allow the bubble to float over the area of the detachment. The purpose of the gas bubble is to push the retina back into its normal position and seal off the area of retinal tear. To ensure the detachment does not reoccur, freezing treatment or laser will be applied after the gas bubble is injected. If the procedure is successful, the retina will be back in its proper position permanently and vision will begin to improve.
Why Would I Need a Pneumatic Retinopexy?
There are many factors that can increase your risk for having a retinal detachment. These factors include:
- Retinal tear
- High Myopia (nearsightedness)
- Weak retinal areas (lattice degeneration)
- Previous detachments in the opposite eye
- Previous cataract surgery
Retinal detachments are typically spontaneous events. However, severe trauma to the eye can cause a retinal detachment.
If a retinal detachment occurs, you may see an increase of floaters that resemble cobwebs. These new floaters may impair your vision. Additionally, you may notice a shadow or grey curtain in your peripheral vision. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is imperative that you see a retina specialist. Reattachment of the retina reestablishes nourishment to the retina allowing your vision to be restored.
Reattachment of your retina by performing a pneumatic retinopexy is less invasive than other surgical interventions. However, the location of your detachment determines if you are a candidate for a pneumatic retinopexy. Patients who have a detachment in the lower part of the eye typically are not candidates for a pneumatic retinopexy. This is due to the gas bubble naturally floating to the upper portion of the eye. Therefore, patients who have a superior retinal detachment may benefit most with a gas bubble injection in the office.
How Is a Pneumatic Retinopexy Performed?
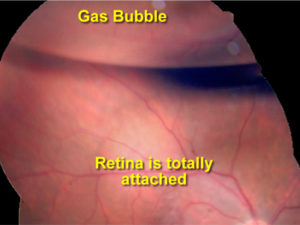
A pneumatic retinopexy is usually a short procedure that takes about 30 minutes. Here is what you can expect during this procedure:
- A full eye exam will take place to identify the area of the detachment and associated retinal tears to ensure you are a viable candidate.
- The eye will be numbed with numbing eye drops and/or injection of local anesthesia to ensure there is no discomfort during the procedure.
- You will be placed into the slit lamp and an anterior chamber paracentesis (AC tap) will take place. During this step, the retinal specialist will insert a small needle into the front of the eye to remove fluid. Removal of this fluid creates space in the eye to allow for the addition of the gas bubble.
- The retina specialist will then inject a gas bubble into the vitreous, the center of the eye, and position you so that the bubble presses on the area of detachment. This positioning allows the bubble to properly float up to the necessary location.
- Once the bubble is in the proper location, your eye will be re-evaluated, and your intraocular pressure will be checked. If the pressure in the eye is elevated, another AC tap may be necessary to relieve pressure in the eye.
- At home positioning and restrictions will be explained to you.
- You will be required to return to the clinic a few days after your gas bubble injection, at which time a laser treatment will take place. This laser is used to permanently seal off the area of the detachment to ensure no future detachments occur in this area.
What Is the Recovery for A Pneumatic Retinopexy?
After a pneumatic retinopexy, you may experience eye irritation or redness for the rest of the day. Over the counter medication can be used to ease any pain you feel after your procedure. You will need close follow-up care with your retina specialist to determine that the retina is properly healing.
It is crucial that you follow all instructions given to you by your retina specialist following this procedure. These instructions will include any restrictions and positioning requirements. You will be required to keep you head in a specific position 3-7 days following a pneumatic. If you have restrictions to the position requirement it is important to discuss this with your retina specialist before you proceed. Other interventions may be available to those who are unable to position for an extended period.
To avoid an increase of pressure in the eye, you will not be allowed to fly, experience a change in altitude, or receive inhaled anesthesia. If you do any of these activities, the gas bubble in your eye will expand, increasing the pressure in your eye. This will cause severe pain and may result in permanent blindness.
It typically takes 3-4 weeks for the gas bubble to naturally dissipate from the eye. Once the gas bubble is gone, you may resume traveling by plane.
What Are the Risk Factors?
Due to pneumatic retinopexy being minimally invasive, most patients have a pleasant experience. However, complications can occur, so it is important to understand the risk factors to this procedure. These risks include:
- Progression of the retinal detachment requiring the patient to undergo surgical intervention
- Recurrence of the retinal detachment
- Elevation of intraocular pressure
- Proliferative vitreoretinopathy – scar like process on the retinal that may cause a new hole or detachment requiring surgical intervention.
In rare cases, a patient may also get a severe infection in the eye that can cause a decrease in vision.
It is important to contact your retina specialist immediately if you are experiencing any of the following:
- Decrease in vision
- Excessive discharge from the eye
- Increase pain, swelling or redness around the eye
- New floaters or flashes
- New shadow or curtain in your vision.
If the pneumatic retinopexy procedure is unsuccessful you may need to undergo further surgical intervention to reattach the retina.
Contact Us!
 A retinal detachment is an eye emergency, and it is imperative that you seek out a retina specialist. Dr. Anita Shane at Venice Retina is trained in diagnosing and treating retinal detachments using the pneumatic retinopexy procedure. She will evaluate your eye and discuss all available options to you. If you are experiencing signs or symptoms of a retinal detachment, contact us today to receive care within 24 hours.
A retinal detachment is an eye emergency, and it is imperative that you seek out a retina specialist. Dr. Anita Shane at Venice Retina is trained in diagnosing and treating retinal detachments using the pneumatic retinopexy procedure. She will evaluate your eye and discuss all available options to you. If you are experiencing signs or symptoms of a retinal detachment, contact us today to receive care within 24 hours.
